The world of financial trading, encompassing crypto, forex, and stocks, is akin to a high-stakes rollercoaster ride. The highs are exhilarating, the lows can be daunting, and the potential for profit is as tantalizing as it is elusive. One of the most intricate aspects of this ride is predicting when the coaster is about to change direction – in trading terms, anticipating trend reversals. Fear not, for we’re here to guide you through this complex landscape. In this comprehensive guide, we’ll delve into three potent reversal strategies that can be your compass in the tumultuous sea of day trading. So, are you ready to embark on this journey? Let’s set sail!
Section 1: Decoding Trend Reversals
The Anatomy of a Trend Reversal
At its core, a trend reversal signifies a fundamental shift in the market’s trajectory. It is akin to witnessing the ebb and flow of waves on a serene shoreline. Picture yourself standing by the beach, observing the rhythmic dance of the waves. In one instance, the waves surge towards you with unwavering momentum, forming an uptrend in the market. However, in the blink of an eye, the tides retreat, receding back into the vast expanse of the sea, marking the onset of a downtrend.
In the dynamic world of trading, recognizing these decisive turning points holds the key to navigating the turbulent waters of financial markets. Just as a skilled surfer identifies the opportune moment to catch the perfect wave, traders strive to pinpoint these pivotal moments to unlock potential profits or protect themselves from undesirable losses.
The ability to grasp the anatomy of a trend reversal is crucial. It involves a deep understanding of market dynamics, meticulous analysis of price movements, and the utilization of effective indicators and strategies. By discerning these pivotal moments accurately, traders gain a competitive edge, positioning themselves to capitalize on emerging trends and make informed trading decisions.
The Significance of Trend Reversals
Trend reversals hold a position of utmost significance within the realm of trading, acting as powerful indicators of a shifting market sentiment. Much like the change in wind direction during a sailing voyage, these reversals carry the potential to alter the course of trading outcomes. Recognizing and capitalizing on these shifts at the earliest opportunity is a fundamental skill for traders seeking to profit from emerging trends.
Market sentiment, driven by a complex interplay of factors such as economic data, geopolitical events, and investor psychology, plays a pivotal role in shaping the direction of financial markets. During an uptrend, where prices ascend with optimism and positive momentum, traders actively seek opportunities to ride the wave of growth. However, as market sentiment shifts, a trend reversal occurs, marking a change in the prevailing winds.
Identifying a trend reversal at its nascent stage allows traders to position themselves advantageously. By staying ahead of the curve, traders can adapt their strategies, adjusting their positions or even reversing them to align with the emerging trend. This proactive approach empowers traders to seize opportunities early, capturing potential profits as the market shifts in a new direction.
Section 2: The Trio of Reversal Strategies

Strategy 1: The Brick of Structure
Visualize the market as a towering wall of bricks, where each brick symbolizes a trading period. Some bricks contribute to the wall’s height (uptrends), while others reduce it (downtrends). The “brick of structure” strategy is about discerning when the wall is on the brink of shrinking.
In this strategy, traders scout for a sequence of lower highs and lower lows in an uptrend (or higher highs and higher lows in a downtrend). This pattern signals that the trend might be on the cusp of a reversal.
Strategy 2: Key Levels
Key levels act as the market’s invisible boundaries, respected by the price movements. They’re price thresholds at which the market has reversed previously. By identifying these levels, traders can foresee potential trend reversals.
This strategy involves sketching horizontal lines at previous peaks and troughs. As the price nears these levels, traders keep a vigilant eye for reversal signs.
Strategy 3: Trend Indicators
Trend indicators serve as navigational tools for traders, guiding them to discern the market’s direction. Renowned trend indicators include the Moving Average Convergence Divergence (MACD) and the Relative Strength Index (RSI).
These indicators generate signals that aid traders in identifying potential trend reversals. For instance, a divergence between the price and the MACD or RSI can hint at a looming reversal.
Section 3: Validating Reversal Signals
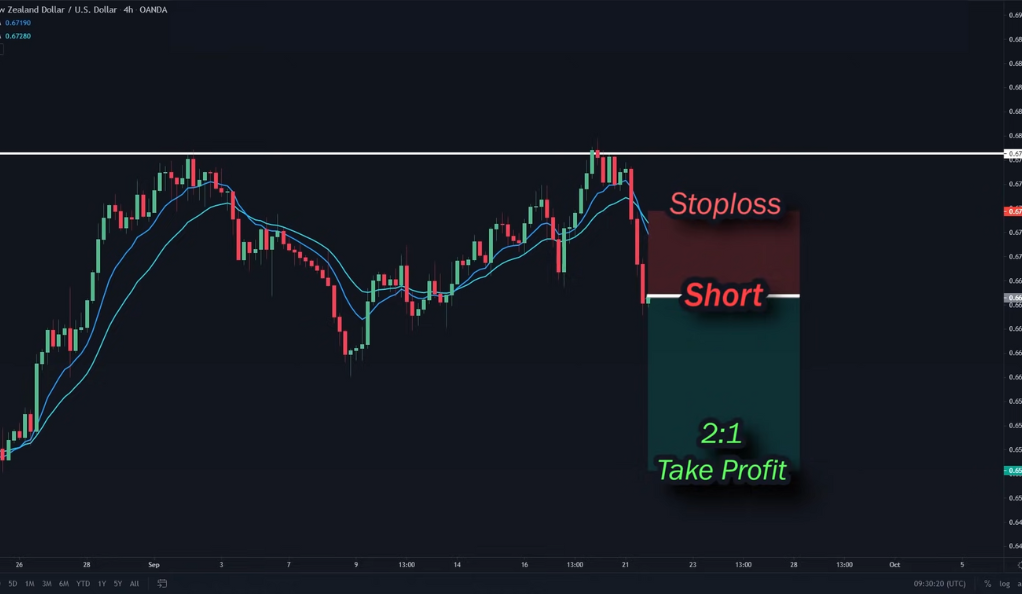
The Imperative of Confirmation
In the realm of trading, the concept of confirmation holds immense importance, comparable to seeking a second opinion. It serves as a critical step in the decision-making process, aimed at validating the legitimacy of a reversal signal before traders commit to a position. Without the safeguard of confirmation, traders run the risk of being lured into a trade based on a potentially deceptive signal.
While identifying a potential trend reversal is undoubtedly valuable, it is essential to exercise caution and avoid hasty actions solely based on initial indications. The market can be unpredictable, and false signals can occasionally emerge, leading traders astray. Thus, confirmation acts as a necessary filter, separating genuine reversal signals from noise.
Techniques for Confirmation
Validating reversal signals is a critical step in the trading process, and there exists a plethora of techniques to enhance confidence in the identified signal. By employing these techniques, traders can strengthen their conviction in the reversal and make more informed decisions.
One commonly used technique for confirmation is waiting for a reversal candlestick pattern. Candlestick patterns provide valuable insights into market sentiment and can validate the anticipated reversal. Examples of reversal candlestick patterns include the doji, engulfing pattern, hammer, and shooting star. These patterns exhibit specific characteristics that suggest a potential shift in the market’s direction. By patiently observing and confirming the presence of these patterns, traders can bolster their confidence in the reversal signal.
Section 4: The Exit Strategy
The Necessity of an Exit Strategy
In the dynamic world of trading, an exit strategy holds tremendous importance as it serves as a vital safety net. It is a premeditated contingency plan that outlines what actions to take if a trade starts to deteriorate. Without a well-defined exit strategy, traders run the risk of allowing a losing trade to spiral out of control, potentially leading to substantial losses.
An exit strategy is akin to a lifeline that helps traders navigate the ever-changing tides of the market. It provides a clear roadmap for managing risk and making informed decisions in the face of adverse price movements. By establishing predetermined exit points, traders can mitigate potential losses and protect their capital.
Crafting Your Exit Strategy

Crafting a robust exit strategy is a crucial aspect of trading that involves defining the parameters for curbing losses and realizing profits. A well-designed exit strategy outlines specific conditions or triggers that prompt traders to take action. These conditions can include predetermined levels of loss or gain, shifts in market conditions, or signals from indicators.
The primary objective of an exit strategy is to protect capital and optimize returns. By establishing predetermined exit points, traders can effectively manage risk and make calculated decisions based on their trading plan. Here are some key elements to consider when crafting your exit strategy:
Stop-loss orders: A stop-loss order is a predefined price level at which a trade is automatically closed to limit losses. It acts as a safety net, preventing further losses beyond a tolerable threshold. By setting a stop-loss order, traders ensure that they exit a losing trade before it erodes a significant portion of their capital.
Profit targets: Profit targets define the desired level of gains at which traders aim to exit a trade. These targets can be based on specific price levels, percentage gains, or other factors. By setting profit targets, traders secure profits and avoid the temptation of greed, allowing them to capture gains and maintain a disciplined approach.
Trailing stop-loss orders: Trailing stop-loss orders are dynamic stop-loss levels that adjust as the trade moves in favor of the trader. They are designed to lock in profits while allowing room for potential further gains. Trailing stop-loss orders automatically trail the price at a set distance, providing a cushion against sudden reversals.
Market conditions and indicators: Monitoring market conditions and utilizing indicators can provide valuable insights for determining exit points. For example, a shift in overall market sentiment, the occurrence of significant economic events, or divergences in indicators can be used as signals to exit a trade. Adapting the exit strategy based on these factors can help traders capture opportunities or avoid adverse market conditions.
Time-based exits: In some cases, traders may choose to exit a trade based on a predetermined time frame. This approach is commonly used in swing trading or when specific events or news releases are anticipated. Time-based exits provide a structured approach and can help manage risk by limiting exposure to volatile market conditions.
Conclusion
Predicting trend reversals in trading is akin to solving a complex puzzle. It demands a profound understanding of market dynamics and a robust strategy. The trio of strategies we’ve explored – the brick of structure, key levels, and trend indicators – can equip you with a sturdy framework for pinpointing potential reversals. However, always remember, confirmation of your signals and a well-defined exit strategy are your safety harnesses in this thrilling ride.
Ainu Token aims to offer impartial and trustworthy information on cryptocurrency, finance, trading, and shares. However, we don't provide financial advice and recommend users to conduct their own studies and thorough checks.

Comments (No)