Artificial Intelligence (AI) technologies have disrupted industries globally, becoming ubiquitous in everyday life. AI drives modern innovations in various sectors ranging from healthcare to finance, transportation, and beyond. Despite the intensive usage and the advancements, distributions of AI products on a global scale face several challenges. Understanding these challenges can shed light on opportunities and offer foresight into the regulatory environment and consumer behavior shaping the global AI landscape.
Analyzing the Key Challenges in Global AI Product Distribution
The first challenge lies in the local regulatory environments, which differ greatly from country to country. AI technology might experience acceptance in one jurisdiction and simultaneously face legal hurdles in another, limiting its distribution. Regulations concerning data protection, intellectual property rights, and ethical standards poses huge challenges to AI distribution, making it a daunting task for businesses to navigate through the regulatory maze.
Another prominent challenge is ensuring security & privacy, two integral aspects in AI products. As AI depends on massive quantities of data, the risk of data breaches significantly increases. The complex nature of these technologies also renders them susceptible to misuse, thus raising concerns over consumer privacy.
The third challenge concerns the development of AI products, specifically a scarcity of the skilled workforce needed to design, develop, test, and deploy AI. While the demand for AI skills has skyrocketed, the supply of specialists has not kept up with this pace, creating a significant skills gap.
The disparity between advanced economies and developing countries in terms of AI distribution widens due to the digital divide. While developed countries showcase rapid advancements and adoption of AI, lesser technologically developed countries struggle, primarily due to inadequate infrastructure, low levels of digital literacy, and lack of necessary regulatory bodies.
Furthermore, ethical considerations surrounding AI applications present well-founded objections to their indiscriminate distribution. The fears of AI causing job losses, enhancing biases, and its approach to privacy could potentially lead to public backlash and resistance.
Last but not least, the variations in consumer behavior across different cultures and economic systems further complicate the global distribution of AI products. The acceptance levels for AI differ among consumers, dependent on the cultural, social, and economic contexts.
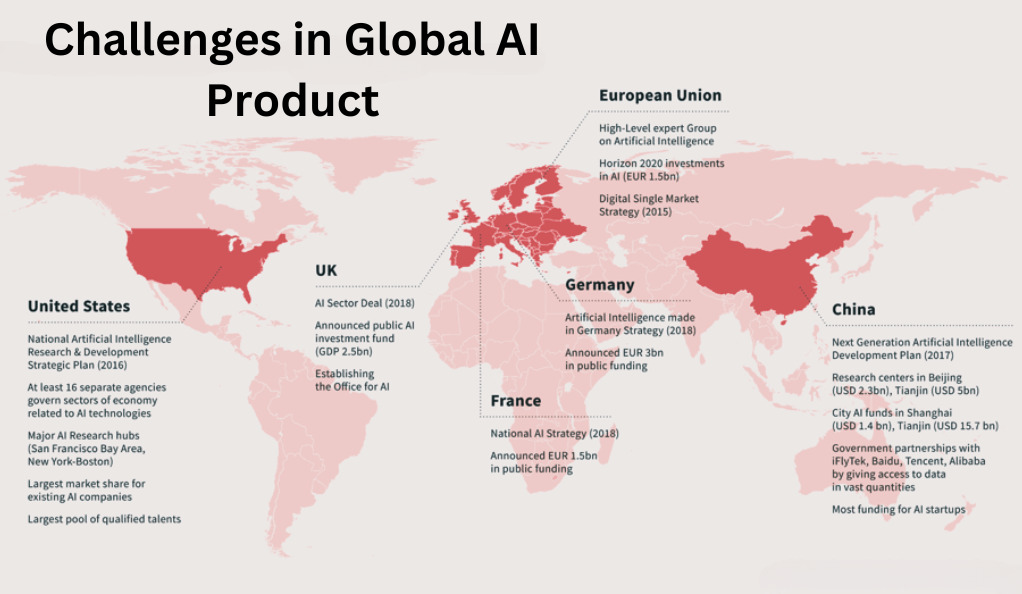
A Thorough Review of Global AI Distribution Issues
The intricate regulatory environment spread across nations can restrict the consistent distribution of AI. The absence of global interoperability standards for AI technologies affects their harmonious dispersion, with the compliance cost associated with local laws being a deterrent for businesses aiming for global distribution.
Privacy and security concerns are elevated due to the comprehensive and intrusive nature of AI, often leading to public discontentment. Ensuring robust cybersecurity measures and transparent data collection practices can mitigate these risks, thereby contributing to a smoother global distribution.
Addressing the AI skills gap issue needs strategic planning. Governments and organizations should take proactive steps like promoting AI education and training, to not only cultivate a skilled workforce, but also to stimulate the economic benefits that come with AI advancements.
Narrowing the digital divide could significantly contribute to a balanced global AI distribution. Investments in digital infrastructure in the developing countries, coupled with initiatives to enhance digital literacy, can play a pivotal role in promoting and disseminating AI equally worldwide.
The ethical dilemmas involved in AI adoption necessitate a carefully curated approach. Policies and guidelines that encourage fairness, transparency, and ethical use of AI will be instrumental in fostering its broad acceptance and in turn, advance its global distribution.
Lastly, understanding the nuances of global consumer behavior is vital. Businesses must customize and localize their AI products to meet consumer needs and preferences, in order to achieve widespread adoption and seamless distribution across varied markets.
In conclusion, while the global distribution of AI products promises untapped possibilities, it’s not without its fair share of challenges. Regulatory complexities, security concerns, skills shortage, digital divide, ethical issues, and varying consumer behavior all influence the distribution process. Regardless of these hurdles, a strategic and comprehensive approach can alleviate the concerns and risks involved. As the world moves further towards digital transformation, a balanced and equitable global AI distribution can bring about significant socio-economic benefits, making it a goal worth aspiring to.
Ainu Token aims to offer impartial and trustworthy information on cryptocurrency, finance, trading, and shares. However, we don't provide financial advice and recommend users to conduct their own studies and thorough checks.



Comments (No)