Layer 3 blockchains are a relatively new concept within the realm of cryptocurrency. They are built on top of existing blockchain networks, such as Ethereum or Bitcoin, and provide an additional layer of functionality and scalability. This article aims to provide a comprehensive understanding of layer 3 blockchains and explore their implications for the crypto industry.
What are Layer 3 Blockchains?
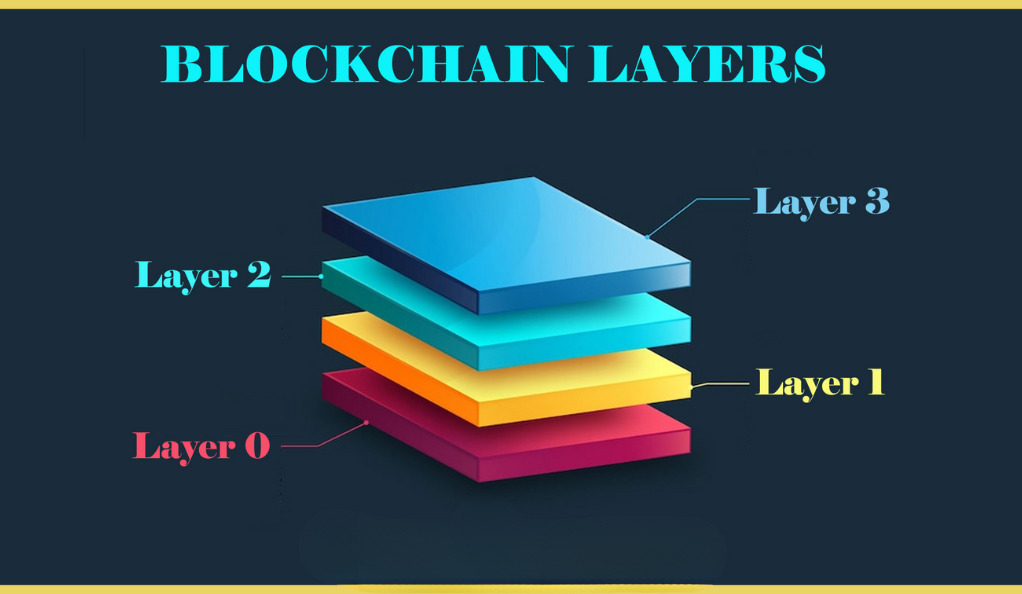
Layer 3 blockchains, also known as off-chain or sidechain solutions, are protocols that operate on top of existing blockchain networks. They aim to address some of the limitations and challenges faced by traditional layer 1 blockchains, such as slow transaction processing times, high fees, and limited scalability. Layer 3 blockchains are designed to handle specific use cases or applications, offering improved speed and efficiency by offloading certain processes away from the main chain.
These layer 3 solutions work by establishing a connection with the underlying layer 1 blockchain and leveraging its security and decentralization features. By moving some computations and data off-chain, layer 3 blockchains can achieve faster transaction speeds and lower fees. Examples of layer 3 blockchains include the Lightning Network for Bitcoin and the Raiden Network for Ethereum.
Exploring the Implications for Crypto
Layer 3 blockchains bring forth several implications for the crypto industry. Firstly, they enhance scalability by reducing the congestion on layer 1 blockchains. By moving some transactions and smart contract executions off-chain, layer 3 solutions can process a higher volume of transactions, thus improving the overall scalability of the network. This scalability improvement is crucial for widespread adoption of cryptocurrencies where slow transaction speeds and high fees have hindered usability for everyday transactions.
Secondly, layer 3 blockchains enable the development of complex and feature-rich decentralized applications (dApps) that were previously impractical to build on layer 1 blockchains. By offloading computations and data storage to layer 3 solutions, dApps can leverage the increased speed and efficiency that layer 3 blockchains offer. This opens up new possibilities for innovation and practical use cases within the crypto ecosystem.
Lastly, layer 3 blockchains have the potential to improve interoperability between different blockchain networks. By acting as a bridge between different layer 1 blockchains, layer 3 solutions can facilitate seamless communication and transfer of assets across multiple networks. This interoperability can contribute to the growth of decentralized finance (DeFi) and other cross-chain applications, enabling users to seamlessly interact with various blockchain ecosystems.
Layer 3 blockchains represent a significant development in the crypto industry as they address scalability and efficiency challenges faced by traditional layer 1 blockchains. By leveraging the underlying security and decentralization of layer 1 networks, layer 3 solutions offer faster transaction speeds, lower fees, and improved scalability. These advancements pave the way for the widespread adoption of cryptocurrencies and the development of more sophisticated decentralized applications. As layer 3 blockchains continue to evolve and gain traction, they are poised to shape the future of the crypto industry and unlock new possibilities for innovation and usability.
Ainu Token aims to offer impartial and trustworthy information on cryptocurrency, finance, trading, and shares. However, we don't provide financial advice and recommend users to conduct their own studies and thorough checks.


Comments (No)